With obesity and Type 2 diabetes continuing to grow as major health problems and causes of early morbidity and mortality, improved studies have examined longer follow-up time periods for diabetes remission after metabolic surgery. Sleeve gastrectomy is a 45-minute laparoscopy procedure.
Ten-year studies help paint a picture of the durability of the remission rates for diabetes among individuals who undergo sleeve gastrectomy. Similar to other published series, the Rodriquez* series shows that remission of Type 2 diabetes is most pronounced one year after surgery and then exhibits gradual erosion of the full remission as the years advance and patients age. While 45 percent of patients have resumed some medications for glucose control at some point over 10 years, 55 percent remain euglycemic and off medication a full decade after sleeve gastrectomy. Other studies show a commensurate slowing of end-organ effects including retinopathy, nephropathy and macrovascular complications.
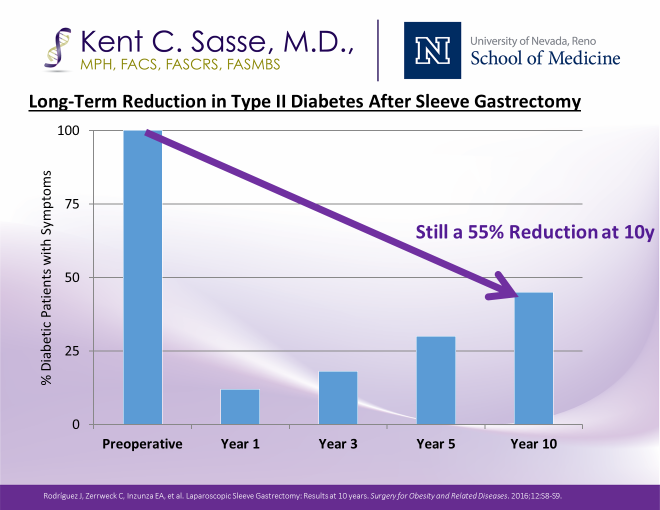
Most but not all, individuals with Type 2 diabetes will enjoy a significant period of remission, defined by euglycemia off of medications. The American Diabetes Association now recommends metabolic surgery for all patients with Type 2 diabetes and a BMI over 35.
In our previous newsletter we examined the NEJM prospective, randomized results of the five-year STAMPEDE trial in which sleeve gastrectomy produced markedly better treatment — and in many cases total remission — of Type II diabetes when compared to intensive medical management at The Cleveland Clinic.
Such long term data reinforce the notion of Type 2 diabetes as a complex, longitudinal disease requiring long-term, multi-disciplinary care with education, exercise, lower-carbohydrate diet, medications and surgery as cornerstone treatment.
These long-term benefits come without the side effects of a bypass surgical procedure. In over 1,600 consecutive laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy procedures, Dr. Sasse has had 0.0% mortality, and in the past 1,300 consecutive sleeve procedures over 4.5 years running, there has been 0.0% rate of the major complication of leak.
The most effective therapy for Type 2 diabetes today is a 45-minute surgical procedure.
“Bariatric surgery’s metabolic effect persists and is more effective at treating Type 2 diabetes in moderate and severely obese patients when compared to medical therapy.” – Dr. Sangeeta Kashyap, MD, Endocrinologist, The Cleveland Clinic.
* Rodríguez, J., Zerrweck, C., Inzunza, E.A., Urbina, D., Palomares, C. and Vizcarra, R., 2016. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: results at 10 years. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases, 12(7), pp.S8-S9.



