In a recent study from the excellent research team at The Cleveland Clinic, investigators reported the results of obese individuals who acquired COVID-19. They compared two matched groups among a total of 363 COVID-19 patients: one group with obesity and one group with prior morbid obesity but having had weight-loss surgery. The findings were significant. No weight-loss surgery patient required the ICU, mechanical ventilation, or dialysis, and none died of COVID-19. Among the matched obese individuals who did not have prior weight-loss surgery, 43 (13.0%) patients required ICU admission, 22 required mechanical ventilation, 5 (1.5%) required dialysis, and 8 (2.4%) patients died.
Obesity is a serious risk factor in COVID-19. As the authors write, “Multiple studies from the United States, Europe, and China have consistently reported adverse clinical outcomes, including higher rates of hospitalization, severe pneumonia, ICU admission, need for invasive mechanical ventilation, and mortality in patients with obesity who develop COVID-19.”
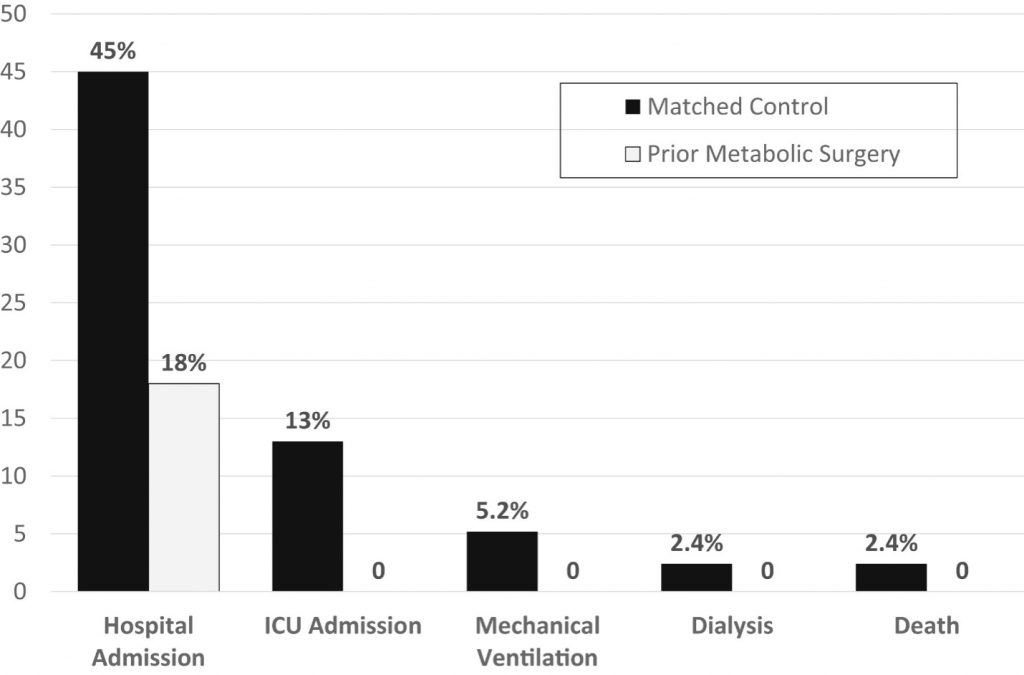
We know that older age and African American race are predictors of clinical severity in Covid-19, but this study found metabolic surgery was a more powerful factor, providing a significant protective effect for infected individuals.
The study led by Aminian found that prior metabolic surgery was associated with lower rates of hospital and ICU admission in patients with obesity who became infected with SARS-CoV-2.
In summarizing their findings, prior metabolic surgery “is associated with lower severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with severe obesity, as manifested by lower risks of hospital and ICU admission. Surgical patients had higher BMIs before metabolic surgery compared with the control group. Without undergoing surgery, they could have had COVID-19 outcomes similar to the control group. After surgery, their BMI decreased on average by 12.6 kg/m2, their metabolic abnormalities improved, and they experienced less severe forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Aminian, A., Fathalizadeh, A., Tu, C., Butsch, W.S., Pantalone, K.M., Griebeler, M.L., Kashyap, S.R., Rosenthal, R.J., Burguera, B. and Nissen, S.E., 2021. Association of prior metabolic and bariatric surgery with severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients with obesity. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases, 17(1), pp.208-214.




